The KMP DINo WiFi is finally here and has full support starting from Souliss v7.2.1 here we describe how get started with this board.
Generally the DINo WiFi can be used as any other ESP8266 based board, but there are some tips that you should not to get started quickly!
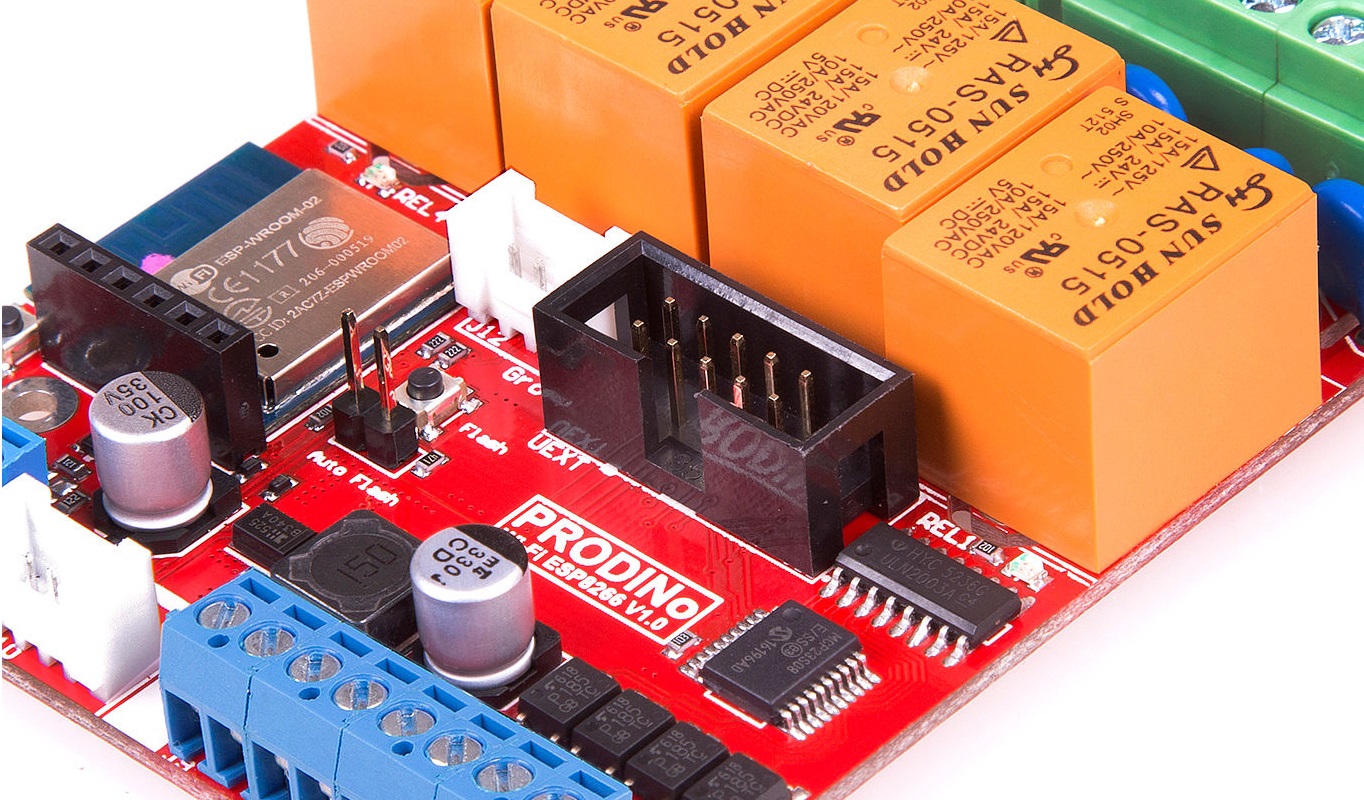
This board is a natural evolution of previous KMP DINo boards that has been largely used with Souliss, we worked closely with KMP while defining the requirements of this board and as result there are Grove and UEXT connector to easily expand the functionality of the board with external sensor and peripherals without additional wiring. As previous KMP DINo boards also the DINo WiFi has relays and opto-isolated inputs, is smaller than previous boards and share a similar switching regulated on-board power supply that goes from 5VDC to 30VDC.
The board comes boxed into a 3 modules DIN rail enclosure.
Loading Souliss on DINo WiFi
The first code upload need an USB to USART converter, next upload can use OTA. The board is not powered from the USART adapter so you need to connect and external power supply every time. The image below show the connection of the power supply wires and the correct position of the USART adapter provided (optionally) with the board.

The pin mapping is the classic one that can be found on many USB to USART adapter, the GND is on the right side of the header and a 3.3VDC adapter shall be used
Near the header used to connect the USB to USART converter there is a jumper and a pushbutton (visible in the below picture), jumping it will allow to program the board. As alternative, power-off the board and press the FLASH button, with the button pressed power-on and then start uploading the code.

Setup the Arduino IDE
Just program this board as any other ESP8266 using the following settings:
- Flash Mode: QIO
- Flash Frequency : 40 MHz
- CPU Frequency : 80 MHz
- Flash Size : 4M (1M SPIFFS)
- Reset Methods : nodemcu
- Upload Speed : 115200
The use of the portable mode in the IDE (just create a folder called portable) is suggested, so that all libraries and cores will be locally installed with in the IDE folder.
You can use the DINo WiFi with Souliss v7.2.1 (or greater) mixing WiFi and RS485 networks, a couple of examples are bundled to build a chain of boards connected via RS485 with a WiFi bridge.
The code below is for the Gateway
This code will connect via WiFi to SoulissApp and via RS485 to the Peers
/**************************************************************************
Souliss - Lights
It handle the four relays either via IN1 to IN4 inputs or using the
Android interface. Connecting the relays to lights or similar electrical
appliance, you can get remote control of them.
Connect multiple ProDINo Wroom via RS485 using the e08_WiFi_Lights_n2.ino
on the peer boards.
Applicable for:
- Light
- Other ON/OFF electrical appliance
Runs on KMP Electronics ProDINo Wroom (WiFi ESP8266)
***************************************************************************/
// Let the IDE point to the Souliss framework
#include "SoulissFramework.h"
#include "bconf/DINo_WiFi_Bridge_RS485.h" // Define the board type
#include "conf/Gateway.h" // The main node is the Gateway, we have just one node
#include "conf/Webhook.h" // Enable DHCP and DNS
#include "conf/DynamicAddressing.h" // Use dynamic address
// **** Define the WiFi name and password ****
#define WIFICONF_INSKETCH
#define WiFi_SSID "mywifi"
#define WiFi_Password "mypassword"
// Include framework code and libraries
#include <SPI.h>
#include <ESP8266WiFi.h>
#include <EEPROM.h>
/*** All configuration includes should be above this line ***/
#include "Souliss.h"
#define LIGHT1 0 // This is the memory slot used for the execution of the logic
#define LIGHT2 1
#define LIGHT3 2
#define LIGHT4 3
void setup()
{
// Init the board
InitDINo();
// Connect to the WiFi network and get an address from DHCP
GetIPAddress();
SetAsGateway(myvNet_dhcp); // Set this node as gateway for SoulissApp
// Define Simple Light logics for the relays
Set_SimpleLight(LIGHT1);
Set_SimpleLight(LIGHT2);
Set_SimpleLight(LIGHT3);
Set_SimpleLight(LIGHT4);
// This node will act as addressing server for the other peers in the network
SetAddressingServer();
}
void loop()
{
// Here we start to play
EXECUTEFAST() {
UPDATEFAST();
FAST_50ms() { // We process the logic and relevant input and output every 50 milliseconds
DigIn(IN1, Souliss_T1n_ToggleCmd, LIGHT1); // Read inputs from IN1
DigIn(IN2, Souliss_T1n_ToggleCmd, LIGHT2); // Read inputs from IN2
DigIn(IN3, Souliss_T1n_ToggleCmd, LIGHT3); // Read inputs from IN3
DigIn(IN4, Souliss_T1n_ToggleCmd, LIGHT4); // Read inputs from IN4
Logic_SimpleLight(LIGHT1); // Execute the logic for Relay 1
Logic_SimpleLight(LIGHT2); // Execute the logic for Relay 2
Logic_SimpleLight(LIGHT3); // Execute the logic for Relay 3
Logic_SimpleLight(LIGHT4); // Execute the logic for Relay 4
DigOut(RELAY1, Souliss_T1n_Coil, LIGHT1); // Drive the Relay 1
DigOut(RELAY2, Souliss_T1n_Coil, LIGHT2); // Drive the Relay 2
DigOut(RELAY3, Souliss_T1n_Coil, LIGHT3); // Drive the Relay 3
DigOut(RELAY4, Souliss_T1n_Coil, LIGHT4); // Drive the Relay 4
}
// Here we process all communication with other nodes
FAST_GatewayComms();
}
EXECUTESLOW() {
UPDATESLOW();
SLOW_10s() { // Process the timer every 10 seconds
Timer_SimpleLight(LIGHT1);
Timer_SimpleLight(LIGHT2);
Timer_SimpleLight(LIGHT3);
Timer_SimpleLight(LIGHT4);
}
}
} The code below is for the Peers
Each of the board running this code will connect to the Gateway via RS485
/**************************************************************************
Souliss - Lights
It handle the four relays either via IN1 to IN4 inputs or using the
Android interface. Connecting the relays to lights or similar electrical
appliance, you can get remote control of them.
Connect multiple ProDINo Wroom via RS485 using the e08_WiFi_Lights_n2.ino
on the peer boards.
Applicable for:
- Light
- Other ON/OFF electrical appliance
Runs on KMP Electronics ProDINo Wroom (WiFi ESP8266)
***************************************************************************/
// Let the IDE point to the Souliss framework
#include "SoulissFramework.h"
#include "bconf/DINo_WiFi_RS485.h" // Define the board type
#include "conf/DynamicAddressing.h" // Use dynamic address
// Include framework code and libraries
#include <SPI.h>
#include <ESP8266WiFi.h>
#include <EEPROM.h>
/*** All configuration includes should be above this line ***/
#include "Souliss.h"
#define LIGHT1 0 // This is the memory slot used for the execution of the logic
#define LIGHT2 1
#define LIGHT3 2
#define LIGHT4 3
void setup()
{
// Init the board
InitDINo();
// Define Simple Light logics for the relays
Set_SimpleLight(LIGHT1);
Set_SimpleLight(LIGHT2);
Set_SimpleLight(LIGHT3);
Set_SimpleLight(LIGHT4);
// This board (peer) request an address to the gateway one at runtime, no need
// to configure any parameter here
SetDynamicAddressing();
GetAddress();
}
void loop()
{
// Here we start to play
EXECUTEFAST() {
UPDATEFAST();
FAST_50ms() { // We process the logic and relevant input and output every 50 milliseconds
DigIn(IN1, Souliss_T1n_ToggleCmd, LIGHT1); // Read inputs from IN1
DigIn(IN2, Souliss_T1n_ToggleCmd, LIGHT2); // Read inputs from IN2
DigIn(IN3, Souliss_T1n_ToggleCmd, LIGHT3); // Read inputs from IN3
DigIn(IN4, Souliss_T1n_ToggleCmd, LIGHT4); // Read inputs from IN4
Logic_SimpleLight(LIGHT1); // Execute the logic for Relay 1
Logic_SimpleLight(LIGHT2); // Execute the logic for Relay 2
Logic_SimpleLight(LIGHT3); // Execute the logic for Relay 3
Logic_SimpleLight(LIGHT4); // Execute the logic for Relay 4
DigOut(RELAY1, Souliss_T1n_Coil, LIGHT1); // Drive the Relay 1
DigOut(RELAY2, Souliss_T1n_Coil, LIGHT2); // Drive the Relay 2
DigOut(RELAY3, Souliss_T1n_Coil, LIGHT3); // Drive the Relay 3
DigOut(RELAY4, Souliss_T1n_Coil, LIGHT4); // Drive the Relay 4
}
// Here we process all communication with other nodes
FAST_PeerComms();
// At first runs, we look for a gateway to join
START_PeerJoin();
}
EXECUTESLOW() {
UPDATESLOW();
SLOW_10s() { // Process the timer every 10 seconds
Timer_SimpleLight(LIGHT1);
Timer_SimpleLight(LIGHT2);
Timer_SimpleLight(LIGHT3);
Timer_SimpleLight(LIGHT4);
}
// Here we periodically check for a gateway to join
SLOW_PeerJoin();
}
} Enjoy!